UMA User Managed Access
This section is in development and is not complete or ready for review.
Token Exchange
NEW CHRIS
Impersonation
Delegation
UMA (User managed Access) V 2.0
[https://build.fhir.org/ig/HL7/smart-app-launch/scopes-and-launch-context.html]
The following two sections (Resource Based Scopes (Scopes) and Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE)) are two additional concepts that should be clearly understood, and they provide additional security controls. Also, PKCE is seen as a security control that will be mandated in future versions of the OAuth 2 specification.
Resource Based Scopes (Coarse Grained Access)
Access and Refresh Tokens provide confirmation that the end-user has consented to delegate access rights to the client. Scopes, which are linked to the Access Token, provided an additional level of authorisation, each one defining a specific capability for example "read” document or "write” document.
Scopes are approved by the end user and enforced by the backend API. The authorisation server validates the token, which contains the scopes that have been consented to, and validates the client is not exceeding its access rights.
Distributed Model - User Managed Access (UMA)
The Distributed Models allows for multiple Resource Servers and Authorisation Servers and is addressed by the User Managed Access (UMA) model, which is driven by the Kantara initiative[4] and currently has been productionised by a number of vendors[5].
UMA is a delegation access model allowing 3rd Parties to have temporary access to resources that are approved (consented to) by the resource owner.
The resource owner has the ability to provide predefined policies that define the relationship and access controls for all their resources across multiple Resource Servers of what can be accessed and by whom (i.e. minimise their interaction in the current OAuth approval process) and provides a central point of control
A centralised UMA Authorisation Server then keeps track of all Resource Servers associated with a given Resource Owner.
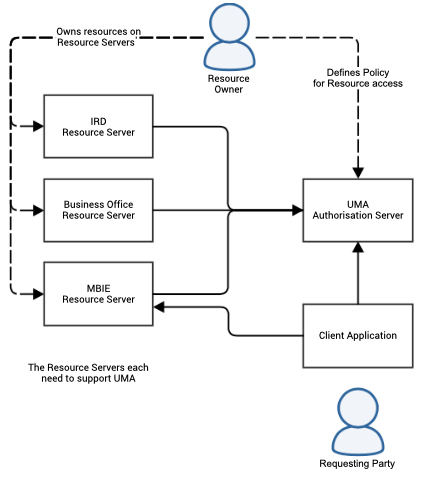
Figure 27: User Managed Access
The Resource Owner establishes a token-based trust relationship between the Resource Server and the Authorisation Server.
The Resource Owner also defines the access control policies which grant access to potential consumers. A client application, driven by the Requesting Party who is requesting access to resources owned by the Resource Owner, attempts to access a resource on a Resource Server but will be redirected to the UMA Authorisation Server.
The client application has to obtain a client key, client secret and access token from the UMA Authorisation Server before trying to get to the required resource on the Resource Server. The Resource Server will validate the access token and the permitted level of access with the Authorisation Server before allowing the client application to consume its required resources.
The UMA Authorisation Server offers two APIs to support these interactions:
-
Protection API – used by Resource Servers for getting authorisation-request tokens and validating access tokens
-
Authorisation API – used by the Client Application to obtain a token for accessing a specific resource
OAuth 2.0 provides a consent model that is driven via a synchronous process, UMA provides enhance consent capability that is driven via asynchronous processes, that allows for:
-
The sharing of information with parties and groups based on relationships
-
Manage request from 3rd Parties
-
Monitor Shares across sources